L
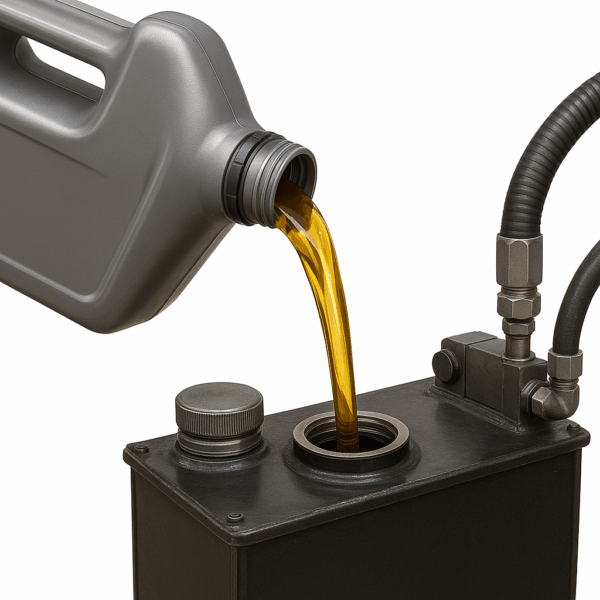
Air Compressor Oil
A compressor oil is used to lubricate both the working parts and the pressurized spaces in a compressor. The purpose of the lubricant in the pressurized section is not only to reduce friction and wear but also to improve sealing of the pressurized spaces and to provide cooling.
For Reciprocating Compressors a lubricant is required for the bearings, pistons, rings, cylinders and valves that has enough antiwear additives and suitable viscosity .The pistons and valves reach temperatures of 2200C to 3000C and the oil film on the surfaces of these components must not form soft and hard carbon.
Good demulsibility properties are also necessary to aide water/oil separation as the oil containing air is cooled and the water vapor condenses.
Calcined (Burnt) Limonite
The final product is supplied in fine powder form with consistent particle size and reliable chemical characteristics suitable for demanding industrial applications. In the paint and coating industry, calcined limonite powder is widely used as a functional filler and natural iron-oxide pigment. Its red-brown to dark brown color tone, excellent heat resistance, and weather stability make it suitable for industrial paints, primers, anticorrosive coatings, and decorative finishes. The powder disperses well in both solvent-based and water-based systems, contributing to color uniformity, opacity, and long-term durability while helping formulators optimize production costs.
Calcined limonite powder is also extensively applied in construction materials, including cement, concrete products, tiles, bricks, and mortars, where it provides stable coloration, bulk density control, and improved thermal performance. In rubber and plastics compounds, it functions as an inert mineral filler that enhances dimensional stability, hardness, and abrasion resistance.
Circulation Oil
Circulating Oil is premium quality, solvent refined, high viscosity index and mineral oils specially chosen for their ability because they play a critical role in lubricating and protecting key components, such as bearings and gears, in systems where a continuous flow of lubricant is required. This continuous flow ensures that moving parts are consistently coated with oil, reducing friction, wear, and heat generation.
Circulating systems need to operate in varying conditions, so it is vital you have a lubrication solution that works consistently no matter the circumstance so they must have Excellent water-separating properties to minimize the formation of emulsions , Good oxidation resistance , good Protection against rust and corrosion , enough foam resistance. Circulation oil has the ability to rapidly separate from water, prevention of emulsion and sludge build up, which hampers lubricating efficiency.
Heat Transfer Oil
- Function:
They circulate through a closed loop system, absorbing heat from a heat source and transferring it to the desired process area, enabling indirect heating. Heat transfer oils are Formulated to promote energy efficient heat transfer performance , to control Oxidation and creating thermal stability that helps resist harmful sludge and coke formation and contributes to long oil service life . Low temperature fluidity assists rapid system start-up , Low vapour pressure at elevated temperatures helps minimise evaporation, vapour lock and pump cavitation and Efficient low pressure operation avoids the need for expensive high pressure pipe-work and heat exchanger systems.
Heat transfer oils have many applications such as used in various industrial processes like plastic molding, chemical reactions, food processing, asphalt production, metal heat treating , food processing , petroleum and wax processing where precise temperature control is crucial.
Hydraulic Oil
Although it is commonly used in the transfer of power, hydraulic fluid can act as a sealant, coolant and lubricant within machinery and equipment. Hydraulic oil can be used for Forklift Trucks ,Log Splitters ,Automotive Lifts ,Wright Standers . Snow Ploughs (Snow Plows) ,Skid Steers (Skid-steer Loader and Skidsteer) ,Aircraft (aviation) ,Air Tools ,Tractors ,Cruise Ships and the Marine Industry. Superior hydraulic oils are available in a wide range of ISO and SAE grades to meet these and many other critical machinery challenges, such as high speed , high pressure , high temperature , very low temperature in winter , turbine – grade temperature and those used for food processing and packaging are available .for a hydraulic oil to be useful it needs to have the below properties:
- Non-compressible
- Thermally stable, within a range of operating temperatures
- Fire resistance
- Non-corrosive & Anti-wearing to its system
- Low tendency to cavitate
- Tolerance to water (resistance to water contamination)
- Total water rejection
- Constant viscosity, regardless of temperature & Long Life
Industrial Filler Grade Limonite
Thanks to its high iron oxide content and earthy yellow-brown to dark brown color tone, limonite powder performs both as a cost-effective filler and a natural pigment in industrial products. In the paint and coating industry, industrial filler grade limonite powder improves opacity, color stability, and film durability while helping to optimize formulation costs. Its good dispersibility makes it suitable for solvent-based and water-based coatings, primers, and industrial paints. In construction materials, limonite powder is widely used in cement, mortar, plasters, tiles, and concrete products, where it contributes to color uniformity, bulk density control, and mechanical strength.
The material is also applied in rubber and plastics compounds, where it functions as an inert mineral filler, enhancing dimensional stability and abrasion resistance. In addition, industrial limonite powder is used in foundry applications, refractory blends, bricks, and ceramic bodies, benefiting from its thermal stability and natural mineral origin.
Industrial Gear Oil
Even when torque is transferred, gears will have sliding and rolling contact, leading to frictional losses and heat generation. Therefore, the lubricants selected for these applications must be able to significantly reduce these frictional losses and cool the gears. Industrial gear oils can be formulated using mineral base oils or synthetic base oils.
Various additives are incorporated into gear oils to enhance their performance characteristics and the viscosity of gear oil is a critical parameter that determines its flow characteristics and lubricating ability. The lubricant must also have a high viscosity at operating temperature such that the formed film can sufficiently support the load while cooling the gears. Another point to consider is the pour point of gear oil ,that refers to the temperature at which the oil begins to solidify and lose its flow properties. Available industrial gear oils can be classified into four main types are Synthetic Gear Oil, Rust and oxidation inhibited (R&O) gear oils, Extreme pressure (EP) gear oils , Compounded gear oils.
Lead Concentrate
Lead is also used in organ pipe making, electric cable coverings, solder for plumbing, lead-acid storage batteries, ammunition, and as a radiation shield in x-ray rooms. Concentration of lead ore happens after the ore is removed from the mine, it is treated at a concentrating mill. Concentrating is generally removing the waste rock from the lead. The ore is crushed and grounded at the mill making it particles of diameters of 0.1 millimeter or less which appear to be finer than table salt, giving it granulated sugar like texture.
Linear Alkyl Benzene (LAB)
Linear alkylbenzene (LAB) is a a family of organic compounds and acost-effective and biodegradable intermediate in the production of detergents and surfactants. Kerosene is the raw material of linear paraffin with high purity, which are finally converted to linear olefins by dehydrogenation. The linear mono-olefins react with benzene in the existence of the catalyst to produce LAB which is used to produce linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS), as a biodegradable detergent.
Linear alkylbenzene (LAB) is produced by reacting benzene with alkyl groups containing 10 to 13 carbon atoms that are derived from normal (straight-chain) paraffins or linear alpha-olefins. Nearly all LAB is converted to linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) by sulfonation
Linoleic Acid
Its renewable nature and functional performance make it a preferred choice in modern, sustainability-focused markets. Commercially, Linoleic Acid is available in refined, distilled, and high-purity grades, suitable for technical, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical uses. Key features include a high degree of unsaturation, excellent skin absorption properties, low melting point, and good emulsifying behavior. Typical technical parameters include acid value, iodine value, peroxide value, moisture content, and fatty acid composition, ensuring consistent quality and processing reliability. Linoleic Acid performs efficiently in esterification, oxidation control systems, and surfactant formulations. Due to its biochemical role, it is highly valued in formulations targeting barrier repair, moisture retention, and improved material flexibility. The product is commonly supplied in drums, IBCs, flexitanks, or bulk packaging to support diverse commercial requirements.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
LNG is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. The liquefaction process involves removal of certain components, such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. The natural gas is then condensed into a liquid at close to atmospheric pressure by cooling it to approximately −162 °C (−260 °F) . The heating value depends on the source of gas that is used and the process that is used to liquefy the gas.
A typical value of the higher heating value of LNG is approximately 50 MJ/kg or 21,500 BTU/lb. A typical value of the lower heating value of LNG is 45 MJ/kg or 19,350 BTU/lb.
Liquorice
Liquorice grows best in well-drained soils in deep valleys with full sun. It is harvested in the autumn two to three years after planting . Licorice root has a long history of use, going back to ancient cultures. It was used traditionally for treating a variety of conditions, including lung, liver, circulatory, and kidney diseases.
Licorice root and extract is promoted as a dietary supplement for conditions such as digestive problems, menopausal symptoms, cough, and bacterial and viral infections. Licorice gargles or lozenges have been used to try to prevent or reduce the sore throat that sometimes occurs after surgery. Licorice is also an ingredient in some products for topical use appliable to the skin. due to its sweetness and flavoring characteristics, licorice extract is mostly used in the confectionery industry.

 Arabic
Arabic