E
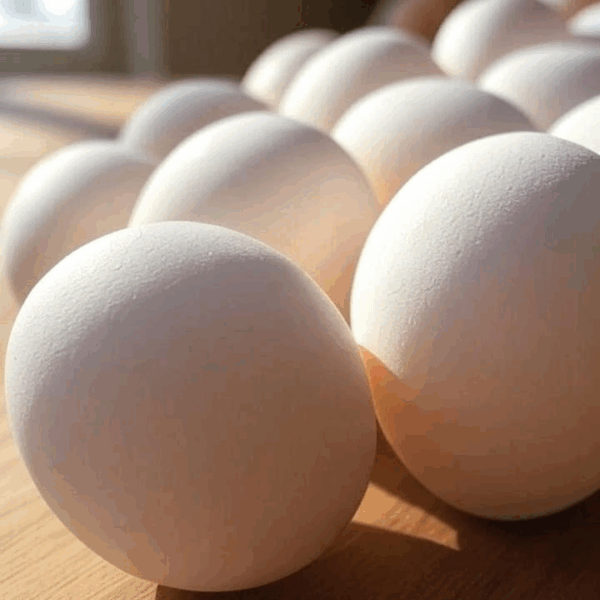
Chicken Egg
Chicken egg is not only an encapsulated product that meets all requirements for the developing embryo, but also a perfect foodstuff with diverse and balanced nutrients along with superior bioavailability for humans.
The whole raw and freshly laid eggs consist of water (76.1%), proteins (12.6%), lipids (9.5%), carbohydrates (0.7%), and ash (1.1%), which are specifically distributed along the shell, egg white, yolk, vitelline membrane, and chalazae, the different components of the egg. Large amounts of proteins are found in the egg white (10.9 g per 100 g) and in the egg yolk (15.9 g per 100 g), including the vitelline membrane, of which these values are slightly modified by the age of hens and their genetic background.
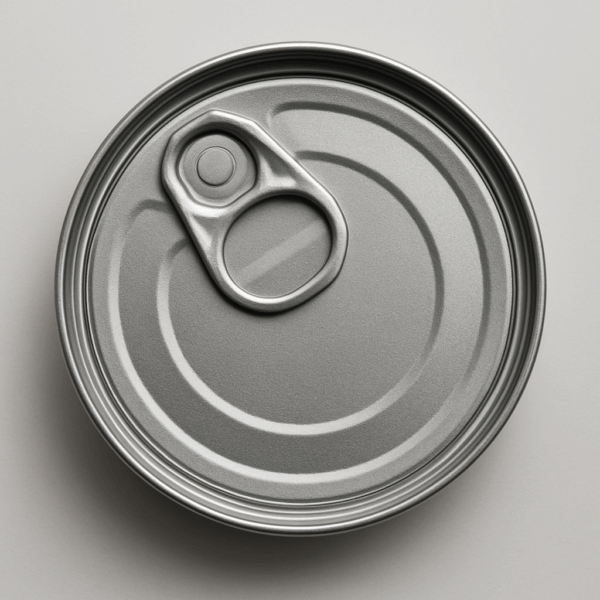
Easy Open End (EOE)
Different types of EOE include peel-off ends, stay-on tabs, and full aperture options depending on the desired opening size and product consistency are available .
Types of Easy Open Ends:
Peel-off end (POE): The entire lid can be peeled off, providing full access to the contents.
Stay-on tab (SOT): A tab remains attached to the lid after opening, reducing litter.
Full aperture (FA): Creates a large opening for easy pouring or scooping.
The material can be tinplate , Aluminum and tin free steel and complete range of shapes can be produced including round, quarter club, oval, pear .
Ends suitable for pasteurization / sterilization / retorting are available. Supplies are made conforming to customer request for client specific usage.
Outside of the EOE can be gold lacquered or clear lacquered. It is also possible for us to supply EZO that are printed with opening instructions or customer LOGO.
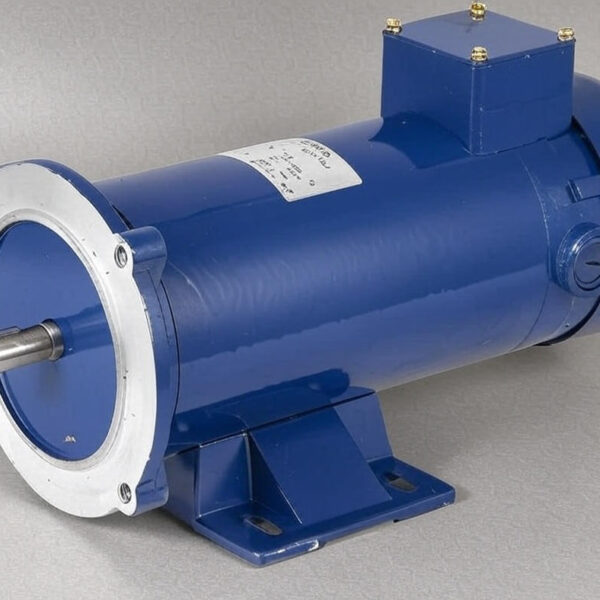
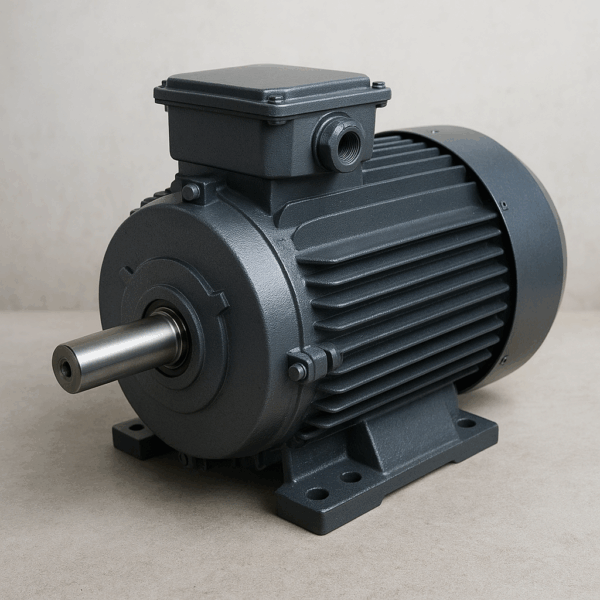
Electric Motor ( DC shunt )
The DC shunt motor is a constant flux motor and it can self-regulate its speed when the load changes, maintaining a steady speed without external modifications.
In a DC shunt motor, the torque is proportional to the armature current, which helps the motor adjust its speed when the load varies. Industrial Use: DC shunt motors are popular in industrial applications where constant speed operation is essential, thanks to their self-regulating speed feature.
One key design feature of the DC shunt motor is its ability to generate high torque. To achieve this, the armature winding must carry a higher current than the field winding, and the field winding must have many turns to increase flux linkage.
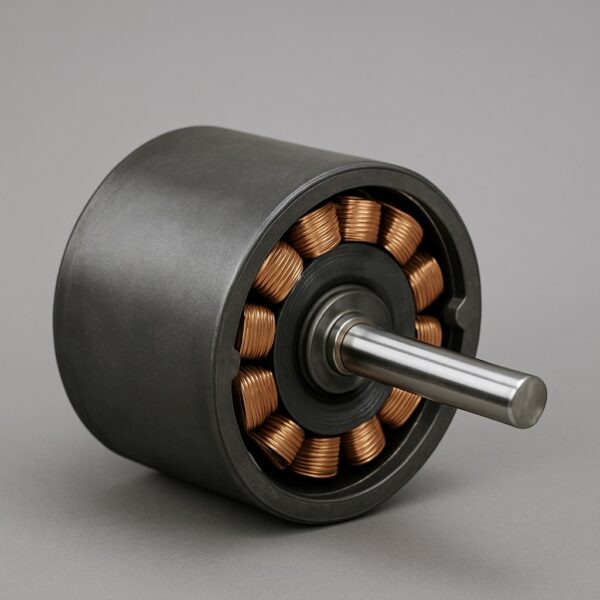
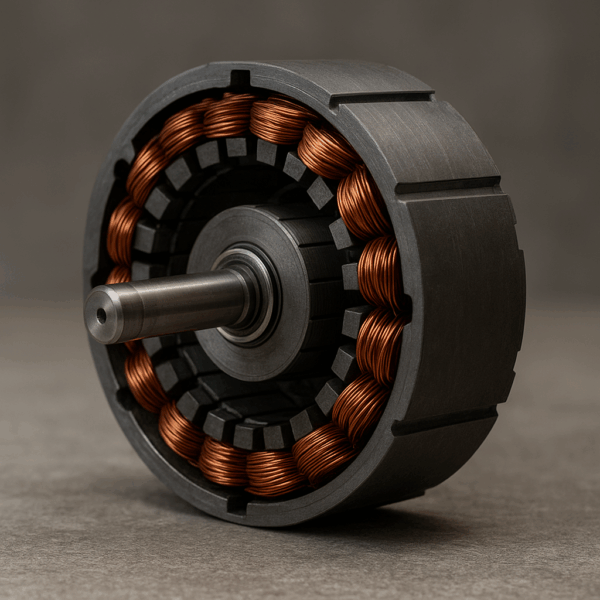
Electric Motor (Asynchronous)
The two main parts of an induction motor are the stator and the rotor. Brass coils are placed in the stator and are separated from each other by ducts of ferromagnetic material. Plastic elements electrically isolate the wires to avoid short circuits. Inside the rotor, horizontal lines are visible, created by the squirrel cage, and foil layers make vertical lines. The bearings hold the crankshaft and the end shields, allowing the rotor to stay at the center stator winding and rotate with minimal friction.
A rotating magnetic field is created around the stator by an AC supply. The relative speed between the stator’s magnetic field and the rotor’s conductors causes an induced electromagnetic field in the rotor conductors. Electricity is induced on the rotor because of electromagnetic induction, not electrical wiring connections. The induced current in the rotor creates an alternating flux around it. The rotor’s flux lags behind the stator’s flux, rotating in the same direction, trying to catch up with the synchronous speed and never reaching it.
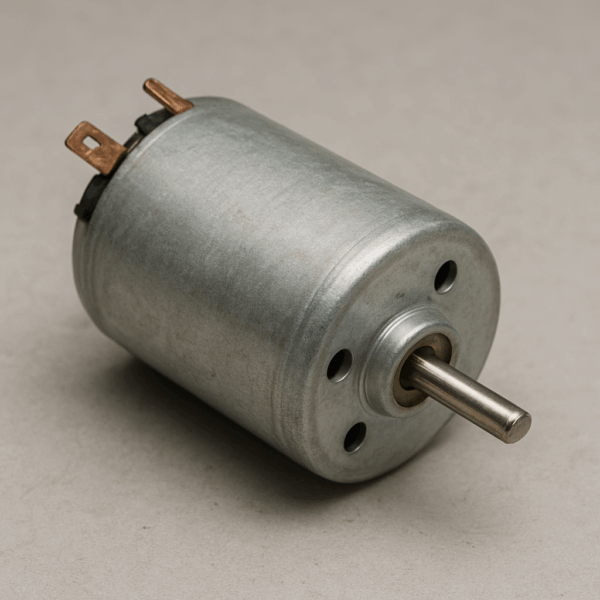
Electric Motor (Brushed DC )
Brushed DC electric motor includes ,Rotor ,Stator ,Inductor ,Armature ,Brushes and Commutator.
According to the stator construction, the brushed motor can be with permanent magnets and with wound stator and according to the wiring diagram of the stator winding, wound field DC motors are divided into:
separately excited DC motor, shunt wound DC motor, series wound DC motor , compound wound DC motor.
Brushed DC motors are High starting torque, Low cost and Well-suited to industrial environments ,so these motors are used throughout many diverse applications, from home appliances to consumer electronics, and especially industrial applications. Their popularity is partially due to how easy it is to vary their speed-to-torque ratio. Additionally, due to the simplicity of their design, they are inexpensive to manufacture and purchase. For this reason, they are used in many applications where the host device will likely fail before the motor.
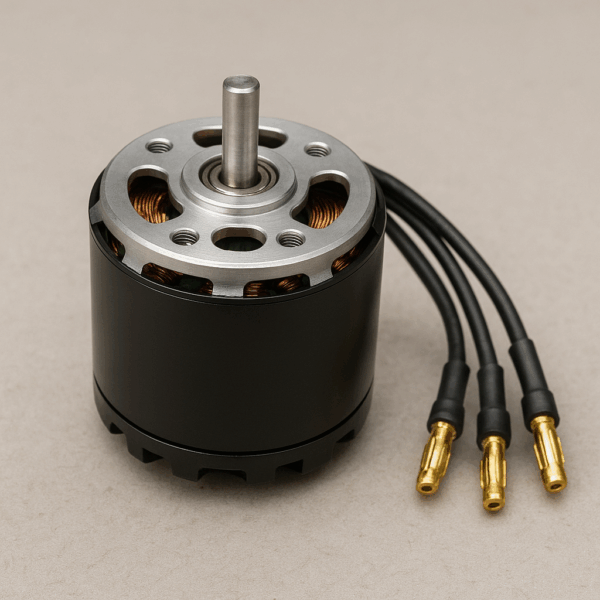
Electric Motor (Brushless BLDC)
The motor’s rotation is managed by a controller that delivers timed bursts of current to the electromagnets in the motor, which in turn controls its speed.
Types of Brushless Motors that are available :
1. Inrunners: Precision in a Compact Package
2. Outrunners: Power Unleashed in Rotation
3. Coreless Brushless Motors: very Light weight
4. Steppers: the choreographers, moving in precise steps
5. Servos Brushless Motors: Precision with a Feedback Beat
6. Synchronous Brushless Motors: Synchronized Strength
Electric Motor (Compound DC )
Compound DC motors are basically made up of a combination of series and shunt motors. they are also called DC compound motors. this type of motor has both series and shunt field coils that are connected to the winding of an armature. These field coils which are linked to the armature windings, afford the essential amount of magnetic flux, and lead to generate the torque necessary to aid the rotation at the desired speed level in the armature. The majority of the field is wound for a shunt field with a few turns of series winding in the top.
The reason behind such a structure amalgamation is to win the better properties of both of these types. A shunt motor brings an extremely efficient regulation for speed, while a series motor has a great and high starting torque. Consequently, a compound DC motor has a great compromise on these features.
Electric Motor (Direct Drive )
This increases the efficiency and creates a quiet and highly dynamic operation as well as a very high lifetime of the system. Examples of Direct Drive Motors are torque motors, linear motors and certain types of BLDC motors. Rotary Direct Drive Motors are used in, Goniometer, Gimbles ,Rotary tables ,SCARA robots , 6-axis robot arms
Linear Direct Drive Motor Applications can be in Various automation applications, Packaging machines , Machine tools , Semiconductor manufacturing equipment. Furthermore, they can also be supplied as frameless motors , these frameless motors are used for situations where small size, low weight, maximum power and optimal speed control is desired.
Electric Motor (For Hazardous Locations )
Also known as explosion proof motors, hazardous location motors play a critical role in protecting workers from potential injuries and even death , since they are designed somehow that work electrically but do not create explosion in hazardous locations
The electric motor is used in hazardous locations must be compliant with standards set out in AS/NZS60079, which is essentially an adaptation of IEC60079 international standards by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Hazardous location motors are indispensable in ensuring that operations run smoothly and safely in these high-risk areas.
Electric Motor (Frameless)
Frameless motors are Compact, lightweight ,Precise in performance , Environmental resilience since they are Embedded directly into the application, frameless motors can be thoroughly protected from caustic washdown fluids, submersion, weather exposure and other environmental hazards.
Two main types of frameless motors that are Frameless outrunner and Frameless inrunner torque motors are in a wide range of diameters, stack lengths and winding variations.
Electric Motor (Gear Motor)
A Geared Motor is a component whose mechanism adjusts the speed of the motor, leading them to operate at a certain speed .
Advantages of the Gear Motor:
- It reduces the speed of the input motor. Micro Motors gear motors have a variety of reduction ratios to select the appropriate speed for your application.
- Availability of multiple combinations of both gearbox and motor at different voltages.
- Having an integrated motor + gearbox solution makes it easier for the end user to develop the machinery and allows him to be able to apply it within his project without wasting time searching for individual parts.
- It is a ready-to-use all-in-one solution that requires no alignment work by the end user.
- Multiplies the torque of the motor. This feature is very important because it allows high torque even in a small space.
Electric Motor (Hysteresis)
Hysteresis Electric Motor can be operated either using a single phase or three phases and in a noiseless operating environment, it maintains a constant speed. The torque generated in the motor is due to the hysteresis and eddy current which is induced due to stator winding.
A hysteresis motor is constructed of five main components:
- Stator
- Single phase stator winding
- Rotor
- Shaft
- Shading coil
There are 4 types of hysteresis motor they are :
- Cylindrical type
- Disk type
- Circumferential-Field type
- Axial-Field type

 Arabic
Arabic